What Foods Have Collagen? A Simple Guide
Keeping your skin young and healthy is important to many. Knowing how diet affects skin health is key. Collagen, a protein, is vital for our skin’s structure. As we get older, our body makes less collagen, causing wrinkles and less flexible skin.
Eating foods rich in certain nutrients helps your skin. Collagen-rich foods and those that boost collagen are key for skin elasticity and health. Krista Goncalves, a certified holistic nutritionist, says, “Diet greatly affects your skin’s look and youth.”
Table of Contents
Understanding Collagen: The Body’s Essential Protein
Collagen is key to keeping our bodies strong. It’s the most common protein in us, making up 25% to 35% of all proteins.
What Is Collagen and Why Do You Need It?
Collagen is a protein that gives our skin, bones, and tendons strength. It’s made of amino acids like glycine and proline. As we age, our bodies make less collagen, causing wrinkles and joint pain.
How Collagen Affects Your Skin, Joints, and Overall Health
Collagen is vital for our skin, joints, and health. It keeps our skin looking young and our joints flexible. Eating foods rich in collagen or taking supplements can help.
| Health Aspect | Collagen’s Role | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Skin Health | Maintains elasticity and hydration | Reduces fine lines and wrinkles |
| Joint Health | Supports cartilage integrity | Reduces risk of osteoarthritis |
| Overall Health | Supports bones, hair, and nails | Promotes overall wellness |
The Science Behind Dietary Collagen
Collagen is a key protein in our bodies, important for skin, bones, and joints. What we eat affects how our body makes and uses collagen. The quality of collagen from food sources is crucial for its effectiveness.
How Your Body Processes Collagen from Food
Your body breaks down collagen from food into amino acids. These amino acids are then used for many body functions. Foods like bone broth have a form of collagen that your body can use quickly, says registered dietitian Carrie Gabriel, MS, RDN.
Different Types of Collagen and Their Functions
There are many types of collagen, each with its own role. Type I is in skin and bones, while Type II is for joints. Knowing about these types helps you choose the right foods for your health.
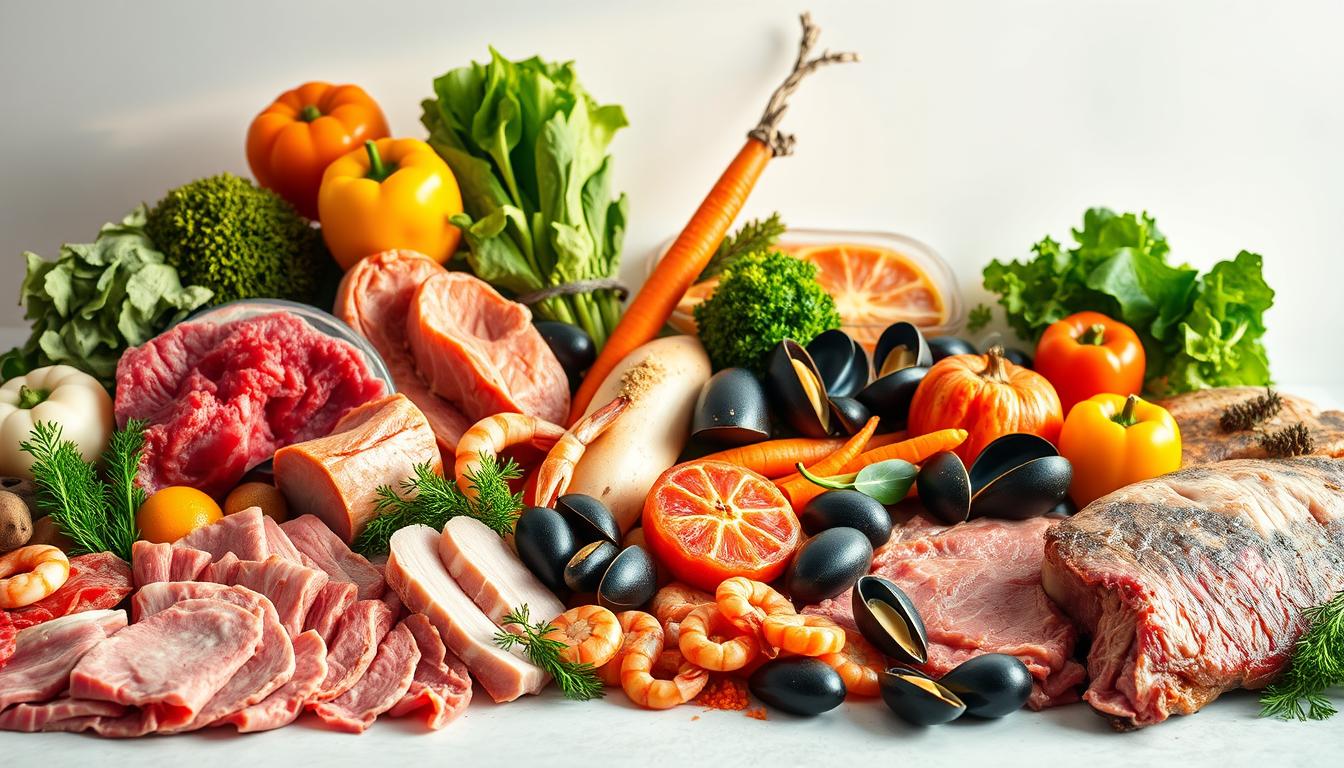
What Foods Have Collagen? Complete List of Natural Sources
Many people think of supplements or bone broth when they hear collagen. But, there are many other foods that offer this important protein. Knowing what foods have collagen helps you make better food choices. These choices support your skin, joints, and overall health.
Some foods are packed with collagen, while others help your body make more. Let’s look at the different types of collagen-rich foods. We’ll see how they can improve your health.
Animal-Based Collagen Sources
Animal-based foods are some of the best collagen sources. Here are a few:
- Bone Broth: A 2019 study found that bone broth isn’t as high in collagen as thought. But, it still has a lot.
- Meat: Tough cuts like pot roast or short ribs are full of collagen. Cooking them slowly breaks down the collagen, making it easier for your body to use.
- Fish and Seafood: Fish skin and scales are great for collagen.
- Organ Meats: Organ meats like liver and kidney are not only rich in collagen. They also have other important nutrients.
These animal sources give you collagen and other key nutrients. These nutrients are vital for your health.
Plant-Based Foods That Support Collagen Production
Plant-based foods don’t have collagen directly. But, they can help your body make more. Here are some examples:
- Vitamin C-Rich Foods: Foods like citrus fruits, berries, and leafy greens are key for making collagen.
- Antioxidant-Rich Foods: Foods full of antioxidants, like berries and green tea, protect collagen from damage.
- Other Nutrients: Foods with proline and glycine, like gelatinous meats and some veggies, also help with collagen production.
Eating these plant-based foods can help your body make more collagen. This supports your overall health.
Bone Broth: The Collagen Superfood
Bone broth stands out among collagen-rich foods for its versatility and nutrients. It’s made by simmering animal bones in water. This process extracts collagen and other nutrients like calcium and magnesium.
This broth is rich in nutrients and has become popular for boosting collagen intake.
How to Make Nutrient-Rich Bone Broth at Home
Making bone broth at home is easy. You need animal bones, water, and optional veggies and spices for flavor. Place the bones in a pot or slow cooker, cover with water, and simmer for 12-24 hours.
The longer it simmers, the more collagen is extracted. You can use bones from beef, chicken, or fish, based on your taste.
Nutritional Benefits: The broth is rich in collagen and also has glucosamine and chondroitin. These support joint health.
Store-Bought Options: What to Look For
If you can’t make bone broth at home, many options are available. Look for products labeled as high in collagen or specify the bones used. Avoid those with preservatives or too much sodium.
Some brands offer collagen-rich bone broth for joint and skin health.
| Brand | Collagen Content | Additives |
|---|---|---|
| Brand A | High | None |
| Brand B | Medium | Preservatives |
| Brand C | High | Sodium-rich |
Fish and Seafood: Hidden Collagen Treasures
Fish and seafood are packed with collagen, a protein key for healthy skin, joints, and bones. Collagen is crucial for our bodies, giving our skin its elasticity, our bones strength, and our joints flexibility. Studies show marine collagen might be more effective for skin health and elasticity.
Fish Skin and Scales: Unexpected Collagen Sources
Fish skin and scales are often thrown away, but they’re full of collagen. The scales, in particular, have collagen similar to ours, making them great for getting collagen through food. Eating fish skin and scales can really help your skin, making it more elastic and reducing wrinkles.
Best Fish Types for Collagen Content
Not all fish is the same when it comes to collagen. Cod, salmon, and halibut are top choices for collagen, with cod being a standout. Adding these fish to your meals can boost your collagen levels, leading to healthier skin, joints, and bones.
Meat Sources of Collagen: Beyond the Obvious
Many think of supplements or bone broth when they hear collagen. But there are many meat sources rich in collagen. Adding these to your diet can boost your health, focusing on joint health.
Organ meats are packed with collagen. Organ meats like liver, kidney, and heart are full of nutrients and collagen. They’re great for traditional cooking and add flavor to your meals.
Organ Meats and Their Collagen Benefits
Organ meats have types I and III collagen, good for skin, hair, and connective tissue. For example, chicken liver is high in protein and collagen. It’s great for your skin and joints.
Chicken cartilage is a top source of type II collagen, which helps joints. Eating chicken cartilage or feet can ease arthritis and keep joints lubricated.
| Organ Meat | Collagen Type | Health Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Liver | Type I, III | Skin, hair, connective tissue health |
| Kidney | Type I, III | Overall health, antioxidant properties |
| Chicken Cartilage | Type II | Joint health, alleviates arthritis symptoms |
Tough Cuts: Why Slow-Cooked Meat Delivers More Collagen
Tough cuts like short ribs or chuck roast are full of collagen. Slow cooking breaks down connective tissue, releasing collagen. This makes the meat tender and the broth rich in collagen.
Slow-cooking tough cuts is a tasty way to get more collagen. Dishes like beef stew or slow-cooked short ribs are not only tasty but also boost your joint health.

Collagen-Boosting Fruits and Vegetables
You can boost your collagen by eating certain fruits and veggies. These foods give your skin the nutrients it needs to stay healthy.
Vitamin C-Rich Foods That Enhance Collagen Synthesis
Vitamin C is key for making pro-collagen, the first step to collagen. Citrus fruits like oranges and lemons are full of vitamin C. Strawberries and kiwis also have lots of it.
Leafy greens like spinach and kale are also good. Adding these to your meals can make your skin look younger and healthier.
Berries, like blueberries, are full of vitamin C and antioxidants. Eating a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables gives you lots of nutrients.
Antioxidant-Rich Plants That Protect Your Existing Collagen
Antioxidant-rich plants protect your collagen from damage. Tomatoes and bell peppers are full of antioxidants. Leafy greens and other veggies are also good for your health.
Eating foods rich in antioxidants helps keep your collagen healthy. A diet full of fruits, veggies, and other nutrients is important for your skin.
Aging and Collagen: How Your Diet Can Help
As we get older, our bodies make less collagen. This affects our skin, joints, and overall health. We might see wrinkles, thinner skin, and stiffer joints.
Why Collagen Production Decreases With Age
Collagen production drops with age for several reasons. These include less cell activity, hormonal changes, and more oxidative stress. This leads to less elastic skin and stiffer joints.
It’s natural for collagen production to slow down with age. But, lifestyle and diet choices can affect this. UV radiation and smoking can make collagen loss worse.
Dietary Strategies to Combat Age-Related Collagen Loss
Eating right can help keep collagen levels up. Foods high in vitamin C, like citrus fruits and berries, boost collagen making. Also, eating foods full of antioxidants, like leafy greens, protects collagen from damage.
Here are some key dietary strategies to combat age-related collagen loss:
- Include vitamin C-rich foods in your diet
- Consume antioxidant-rich foods
- Stay hydrated to maintain skin health
| Nutrient | Food Sources | Benefits for Collagen |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C | Citrus fruits, berries, kiwi | Enhances collagen synthesis |
| Antioxidants | Leafy greens, tomatoes, bell peppers | Protects collagen from oxidative stress |
| Omega-3 fatty acids | Fatty fish, flaxseeds, chia seeds | Reduces inflammation, supports joint health |
Collagen for Joint Health: Best Food Sources
You can help your joints by eating foods rich in collagen. Collagen is a key protein that keeps your joints, bones, and tissues strong. As we get older, our bodies make less collagen, which can cause joint pain and stiffness.
How Dietary Collagen Supports Joint Function
Dietary collagen, like type II found in chicken cartilage, is key for healthy joints. Type II collagen is great for joints and might ease arthritis symptoms. Eating collagen-rich foods lets your body use amino acids to fix and strengthen joint tissue.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods That Protect Joint Collagen
Eating foods that fight inflammation can also protect your joints. Foods like salmon and berries are full of omega-3s and antioxidants. They help lower inflammation and keep your joints healthy.
| Food Source | Collagen Type | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Chicken Cartilage | Type II | Supports joint health, alleviates arthritis symptoms |
| Fish (salmon) | Type I | Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, reduces inflammation |
| Bone Broth | Type I, II, III | Rich in collagen, supports joint and bone health |
| Berries | – | Rich in antioxidants, reduces inflammation |

Common Myths About Collagen in Foods
Have you heard many claims about collagen in foods? But how true are these? Nutrition is full of myths, and collagen is no different. It’s key to rely on science to understand the truth.
Debunking Collagen Misconceptions
Some think eating collagen-rich foods improves skin and joints. While collagen is vital, the body processes it differently. Research shows that supplements might be better for collagen levels than food.
It’s important to know fact from fiction about collagen sources. Not all foods are as collagen-rich as claimed. For example, bone broth’s collagen content varies with how it’s made.
Science-Backed Facts About Dietary Collagen
Eating foods rich in vitamin C, proline, and glycine helps make collagen. Citrus fruits, leafy greens, and lean proteins are good for collagen. Also, antioxidants protect collagen from damage.
Knowing the science behind collagen helps you choose better. Focus on whole foods and understand supplements’ benefits and limits. This supports your health and well-being.
Collagen Supplements vs. Natural Food Sources
Choosing between supplements and whole foods for collagen is important. Both can boost your collagen levels. But, some might be better for you than others.
Wondering if to eat collagen-rich foods or take supplements? Knowing the pros and cons of each can guide you. This helps match your choice with your health goals and lifestyle.
When Supplements Make Sense
Collagen supplements are great in some cases. For example, if your diet is limited, supplements can help. They’re also good for joint pain or skin problems.
Research shows supplements can improve skin and joint health. When picking a supplement, choose ones with good reviews and high-quality collagen peptides.
How to Choose Quality Collagen Products
Finding the right collagen product can be tough. Here are important things to look for:
- Choose products from trusted brands with clear sources and making processes.
- Make sure they’ve been tested by third parties for quality and purity.
- Think about the collagen type: Type I is good for skin, Type II for joints.
| Product Feature | Collagen Supplements | Natural Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Convenience | Easy to consume, portable | Requires meal planning and preparation |
| Cost | Can be expensive, even for top-quality ones | Often cheaper, with more nutrients than just collagen |
| Nutritional Value | Provides collagen peptides | Offers a wide range of nutrients, not just collagen |
Conclusion: Optimizing Your Diet for Collagen Health
Eating foods rich in collagen can greatly improve your health, focusing on your skin and joints. Chicken, fish, bone broth, and egg whites are great sources. They help keep your skin healthy and your joints working well.
Plant-based foods like citrus fruits and leafy greens are also key. They boost collagen production, making your skin look better and your joints stronger.
Studies show that enough protein and nutrients like copper and zinc are vital. They help your body repair and renew tissues, including collagen (source). By choosing the right foods, you can help your body make more collagen. This leads to better skin, stronger joints, and overall health.
To make your diet better for collagen, eat a variety of collagen-rich and nutrient-dense foods. This balanced diet will help you enjoy the benefits of collagen for your skin and joints. It will improve your life quality.